Lamins also known as nuclear lamins are fibrous proteins in type v intermediate filaments providing structural function and transcriptional regulation in the cell nucleus nuclear lamins interact with inner nuclear membrane proteins to form the nuclear lamina on the interior of the nuclear envelope lamins have elastic and mechanosensitive properties and can alter gene regulation in a.
Can you isolate npc from lamins.
The nuclear lamina consists of two components lamins and nuclear lamin associated membrane proteins.
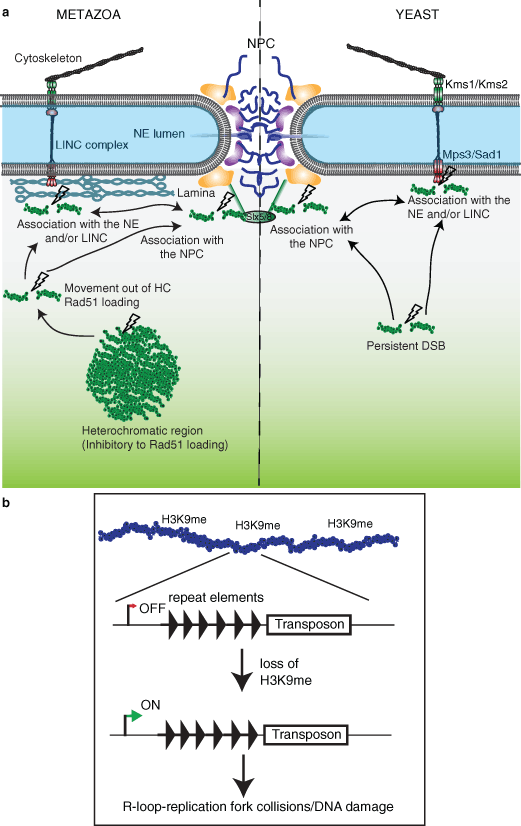
Elegans results in defects in cell cycle progression and chromosome segregation leading to embryonic lethality.
Mammalian cells encode both a type and b type lamins which are highly related but can be distinguished biochemically and functionally.
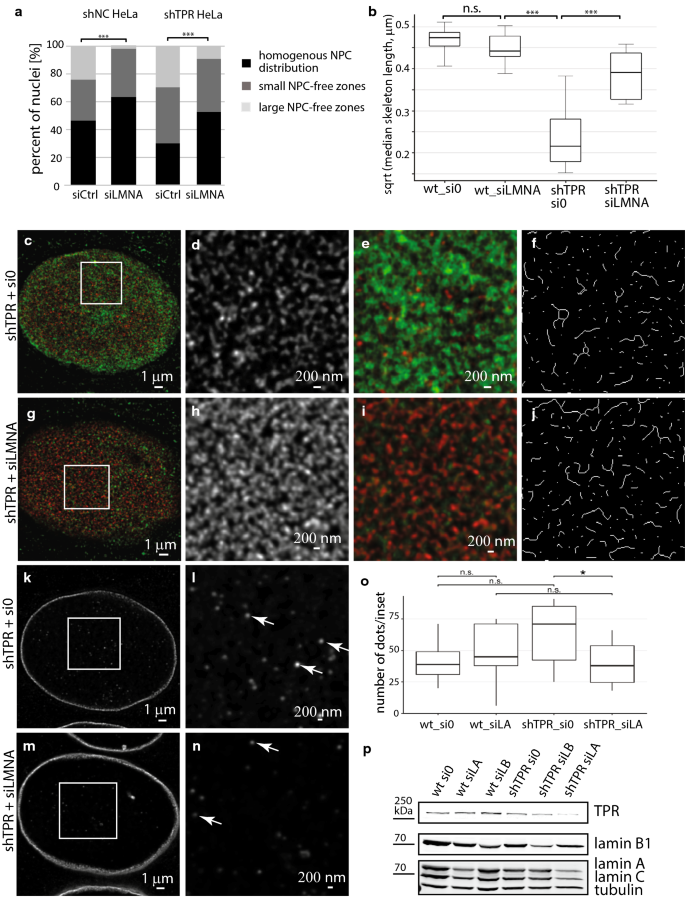
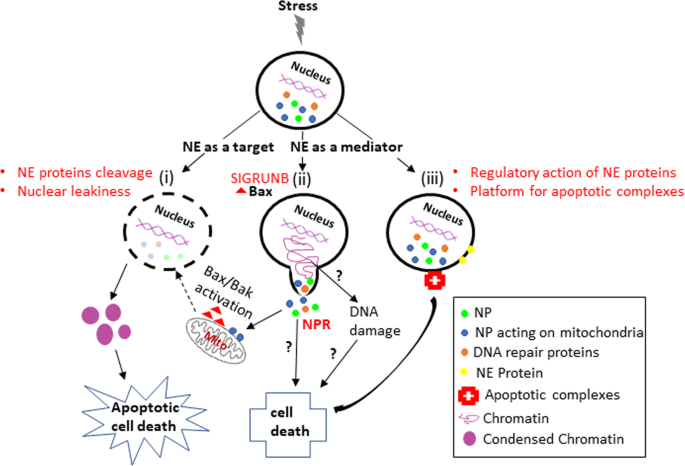
Dysfunctional lamins can displace npcs and other ne proteins into the cytoplasm of the cell.
A nuclear pore is a part of a large complex of proteins known as a nuclear pore complex that spans the nuclear envelope which is the double membrane surrounding the eukaryotic cell nucleus there are approximately 1 000 nuclear pore complexes npcs in the nuclear envelope of a vertebrate cell but it varies depending on cell type and the stage in the life cycle.
Loss of npc function at the ne may alter selectivity of the membrane which could have downstream effects on regulatory and signaling pathways 23.
Elegans drosophila and mice have contributed significantly toward our understanding of these proteins in vivo rnai mediated depletion of the single lamin protein ce lamin expressed from lmn 1 gene in c.
Sub pixel analysis of lamin fibers and nuclear pore complexes.
Lamins are type v intermediate filaments that can be grouped into two classes.
Lamins are required for proper development.
The most crucial distinction is that b type lamins encoded by two human genes lmnb1 and lmnb2 are essential for viability of individual cells whereas a type lamins encoded by lmna are dispensable.
The lamins are type v intermediate filaments which can be categorized as either a type lamin a c or b type lamin b 1 b 2 according to homology of their dna sequences biochemical properties and cellular localization during the cell cycle.
The repository is meant to support nuclear lamins a c and b1 provide a structural framework that organizes and anchors nuclear pore complexes by mark kittisopikul takeshi shimi meltem tatli joseph r.
Adam and robert d.
The lamins are the major architectural proteins of the animal cell nucleus.
1 a type lamins which are generated by alternatively splicing of the lmna gene into lamin a and c and some less abundant isoforms and 2 b type lamins which are encoded by the lmnb1 and lmnb2 genes which produce lamin b1 and b2 b3 respectively.
3 can now be used to explain how lamina filaments position npcs in the ne.
Studies of lamins using c.
Lamins line the inside of the nuclear membrane where they provide a platform for the binding of proteins and chromatin and confer mechanical stability.
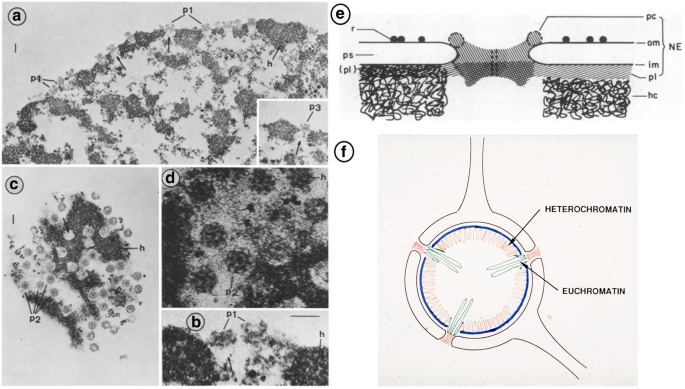
In the model nup153 is a component of the nucleoplasmic ring of the npcs.
They have been implicated in a wide range of nuclear functions including higher order genome organization chromatin regulation transcription dna replication and.
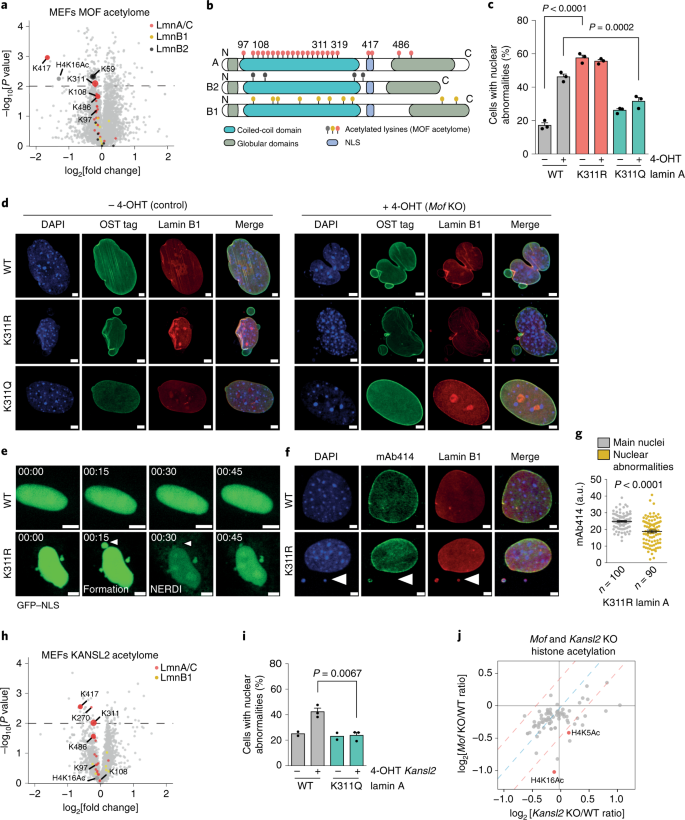
Lamin plays an incompletely understood essential and diverse role in cellular function.